Recognising an acute leukaemia heavily depends on your
ability to make the distinction between different textures, colours and shapes!
Take a look at this photo of a blast cell (upper left) seen in an Acute Myeloid Leukaemia and a mature neutrophil (cell that looks like a happy face, bottom right). Notice the nucleus. The blast cell has
chromatin in the nucleus that is very spread out, almost looks as if dots have
been made with a fine pen. Compare this to the neutrophil. The chromatin in the
nucleus have condensed, showing lots of texture. To me it almost looks like
knots!
Blasts often have spherical inclusion in the nucleus called a nucleolus, which can be seen on the cell above over to the left side. This also tells us we are looking at an
immature cell.
Scientists use this along with features such as size of cell
and size of nucleus compared to cytoplasm, in order to recognise an immature cell.
From there we need to take this further and distinguish
which type of Acute Leukaemia we could be dealing with and again this about
recognising subtle features. Look at this picture. The little red ‘comma’ like
inclusion in the cytoplasm is called an auer rod. This tells us that this is an
Acute Myeloid as opposed to an Acute Lymphoid Leukaemia.
To go further it is possible morphologically to determine
more about the type of Acute Myeloid Leukaemia we are dealing with, by looking
at shapes and colours and this leads me onto today’s film which my colleague
very kindly saved for me . It’s an Acute Promyelocytic Leukaemia (APL). It is
vital that the distinctive morphology is not missed as APL is a haematological
emergency.
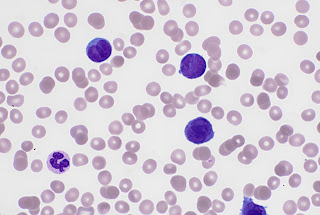
There are two types
of APL, one has abnormal promyelocytes with numerous granules, whilst the other
which we have here is the variant form and the blasts have distinctive bilobed
nuclei and appear to lack granules. The morphology of the variant is quite distinctive and should always be on the Scientist's mind when assessing a blood film for a new leukaemia.
APL is a haematological emergency as it can be rapidly
fatal due to bleeding and thrombotic complications. This patient indeed had a
D-Dimer result of 2560 ng/ml. Suggestive of DIC. In DIC clotting factors are
abnormally consumed which leads to not only bleeding but also thrombotic issues.
Bleeding into the brain or lungs or clots blocking the heart, brain and lungs can
be life threatening.
I’ve been reading an article that explains APL quite nicely
at https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/acute-promyelocytic-leukemia.
I didn’t know the actual reason behind the coagulation
issues in APL but it appears that on the surface of the abnormal promyelocytes
is tissue factor which contributes to the activation of the clotting cascade.
Also Annexin II, present on the surface of the promyelocytes activates plasmin
which breaks down blood clots. The activation of these two leads to excessive
clotting, excessive bleeding and excessive breaking down of clots.
The treatment for this type of leukaemia uses a derivative
of vitamin A which matures the promyelocytes to mature neutrophils! This
treatment is called al-trans-retinoic acid or ATRA. This is because most patient’s with APL, alterations
in the RARA gene occur, which is involved in using vitamin A to mature blood
cells. The alteration to the gene occurs where the RARA and PML genes are
located leading to the PML/RARA fusion gene. This leads to abnormal vitamin A and
stops maturation of the promyelocytes, leaving them in effect ..stuck! Pretty clever
treatment based on understanding the role of the RARA gene.





No comments:
Post a Comment